On screen, Chinese boxers fight for glory - and themselves
|
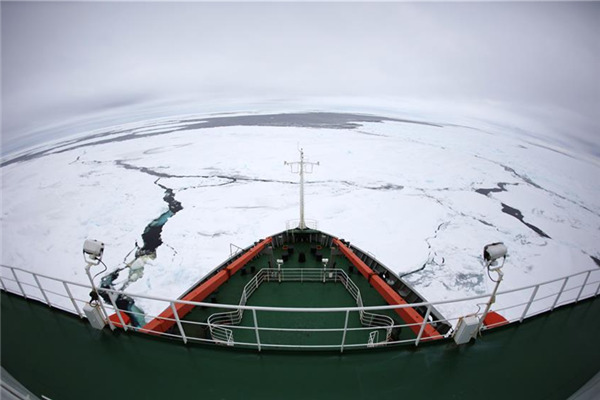
Boxer Qi Moxiang fights Akihiro Matsumoto of Japan in a 2001 bout in Huili County, Sichuan province, that is chronicled in the documentary China Heavyweight, directed by Yung Chang. Liu Yang For China Daily |
Boxing was banned in China in 1959, criticized as brutal and capitalistic. The ban wasn't lifted until after Muhammad Ali visited the country 20 years later, leading Deng Xiaoping to declare, "If we want to win friends, if we want to win respect, we have to win medals."
In 1987 the China Boxing Association was founded, restoring the sport to official status and opening the ring to amateur and professional fighters.
Deng's words resonate today in the extreme reverence paid to Chinese Olympic champions, who are treated as national heroes. Participation in international sports competitions has become an important public symbol of China's standing in the world.
It is within this context that Yung Chang, the Chinese-Canadian director of the award-winning 2007 documentary Up the Yangtze, set out to make a film about boxing, a sport that is by nature fiercely individualistic.
In China Heavyweight, which was screened at New York's Symphony Space on Aug 12, a coach tells prospective boxers: "You will be the country's official athletes. You will be the country's people. If you don't train hard, you'll end up growing tobacco. Then you won't be anyone but your mama's kid."
For so many young Chinese boxers - often recruited in adolescence - the sport represents a chance to rise up in the world and escape the field work to which their parents are bound.
In Huili County, we meet Miao Yunfei, who idolizes "boxing kings" like Mike Tyson and Manny Pacquiao. "I don't want to stay in this backward place," he tells his parents. He Zongli, whose emotional strength is called into question by his coaches, yearns for Olympic glory. Both train under Qi Moxiang, who nurses his own boxing dreams even as he cautions his charges against being too driven by glory.
"I realized there was a bigger story to tell here," Chang told China Daily. "To me, it seems to mirror the notion of the rise of the individual in China. It is an individualistic endeavor, in a country that is rapidly undergoing change."
Chang recounted the words of a professional coach. "He told me that when he recruits fighters, he always asks them, 'Who are you fighting for?' If they say they're fighting for their country, he shows them the way out. If they say they're fighting for themselves, they're allowed to continue training."
And yet for those who remain on the amateur circuit, training remains a collective undertaking, with fighters living and boxing together as a unit in government facilities.
"In China, competing for national excellence is almost a religion," said China Heavyweight producer Yi Han in an interview with China Daily. "But with boxing, the bottom line is that you're fighting for yourself. When a boxer steps into the ring, he's defending and fighting for himself, not anyone else.
"As the boxers in the film come of age, should they fight for the collective good as amateurs or for their personal grain as professionals? The story is a metaphor for nationalism versus individualism that everyone faces in China," Yi said.
This conflict is central to the development of young boxers, explained Chang. "On one level they are sacrificing for their country, on another level for their family, and then on the next level for themselves," he said.
All of these teenagers will at some point have to decide between remaining in the amateur system or making the jump to professional fighting.
"It's a way out, a chance to improve the lives of themselves and their families," Yi said. "So they are willing to 'eat bitterness' and train very hard. Only a handful can make it to the top of the pyramid. Years of hard training may end in vain. In a country where money has become a religion, these boxers will have to fight very hard against the financial pressure from their family and society."
Yi expects boxing to grow in popularity in China. State boxing regulators have begun working on ways to promote the professional version of the sport on a larger scale, she said, pointing out that weekly rebroadcasts of pro fights already enjoy an audience of 30 million.
The film has enjoyed a warm reception in the US. The New York Times called it a "remarkably tender portrait"; The New York Post deemed the film "Rocky, Asian style."
For Chang, boxing is a microcosm of life,
"So often for boxers, it's a story of impoverished people fighting their way out of poverty," he said. "It's a classic tale. I was interested in taking that Western idea and placing it in the realm of a Chinese story."
This rags-to-riches element of the documentary rang true with Tyson, who Chang met in China while working on the film. He recounted meeting the American ex-heavyweight in 2010 in Tianjing, where Tyson had been hired to serve as a temporary ambassador for the sport. For three days, Chang camped outside Tyson's luxury hotel, making inroads with members of the boxer's entourage. On his last day in China, Tyson requested three items: a toenail clipper, a pomegranate, and a Shaw Brothers kung fu movie. His entourage asked Chang to help; the director failed to find any of the items but he did present the boxer a copy of Up the Yangtze. He later showed Tyson footage from "China Heavyweight".
"He was moved by the footage and said that these were the same experiences he'd gone through as a poor kid fighting his way up and out," he said. Tyson, who has a tattoo of Mao Zedong on his arm, became interested in China while incarcerated in the mid-1990s on a rape conviction, Chang said.
The demo included a clip of Don King, the legendary boxing promoter and former manager whom Tyson sued for $100 million in 1998. When Tyson finished watching the footage , he told Chang: "Don King is Chiang Kai-shek and I am Mao Zedong, and I'm going to kick him out of China."
kdawson@chinadailyusa.com