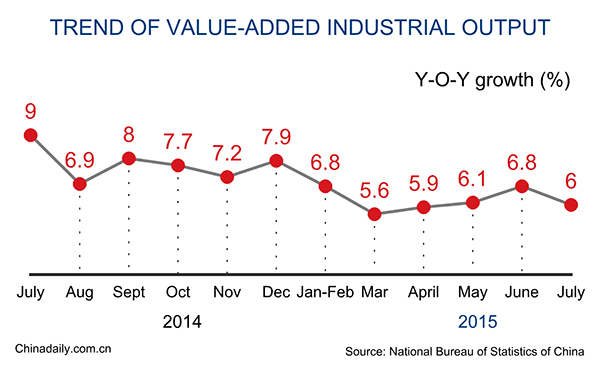
BEIJING - China's value-added industrial output expanded 6 percent year on year in July, down from 6.8 percent for June, the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) said Wednesday.
The decline in output growth ended a trend of steady recovery reported in the second quarter of this year.
NBS statistician Jiang Yuan attributed the drop mainly to flagging external demand, a weak property sector and less production of some consumer goods, including automobiles and cigarettes.
Year-on-year growth in the first seven months stood at 6.3 percent, the same level as the growth for the first half of the year.
China uses value-added industrial output to measure the final value of industrial production, or the value of gross industrial output minus intermediate input, such as raw materials and labor costs.
The NBS data only tracks the output of large Chinese companies with annual primary business revenues of more than 20 million yuan ($3.16 million).
The figures also showed that industrial output in China's western regions increased by 7.9 percent in July, trailed by 7.4 percent in central areas and 6 percent in eastern regions.
In a breakdown, manufacturing output rose 6.6 percent, mining output added 5.6 percent, while output of electricity, heating, gas and water sectors dropped 0.2 percent, the bureau said.
