China's trade surplus figures 'over-inflated'
Hot money inflows, disguised as trade payments, distort numbers
China's trade surplus figures in the first four months of the year were over-inflated by hot money smuggled into the country to profit from interest rate differentials and investments in the real estate and financial sectors amid the yuan's appreciation, according to economists.
If the fake transactions, which were disguised as trade payments, are not taken into account, the real surplus for January-April was about $6 billion, about one-tenth of the official $61 billion figure, said Lu Ting, an economist at the Bank of America Merrill Lynch in Hong Kong.
That would be the smallest trade surplus figure in the January-April period after the country reported a $10.8 billion deficit in 2004, Lu added.
In 2012, China's trade surplus was $18.8 billion for the first four months.
Lu's estimates are based on the assumption that the country's actual exports in the first four months increased 5 percent year-on-year, compared with the official 17.4 percent figure, and that actual imports rose 7.6 percent year-on-year, also lower than the official 10.6 percent figure.
China's trade data have been the target of skepticism in recent months from Hong Kong to Wall Street. Some analysts have said that they believe that Chinese exporters brought in speculative money by overstating export payments and arbitraged the differential between the yuan and the HK dollar by transporting goods in and out of Hong Kong.
"Exports were definitely inflated in the first four months, and mainly driven by shipments to Hong Kong," said Li Jian, a researcher from the Chinese Academy of International Trade and Economic Cooperation, a think tank of the Ministry of Commerce.
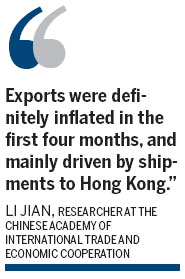
"Exporters over-reported the prices of exports or repeatedly exported the same batch of goods to bring in hot money as the interest rates are much higher than in many other countries."
A source with the General Administration of Customs, who declined to be named, told China Daily that "there was inflation in the export data in the first four months, which was basically caused by abnormal shipments to Hong Kong, with the surge in gold imports and exports also to blame".
Lu said in a May 10 report that shipments of gold between the mainland and Hong Kong were used by exporters to arbitrage the difference between the onshore and offshore exchange rates for the yuan as the valuable metal. The method, which has low transportation costs, is an ideal channel for speculative money flows.
In April, exports to HK grew 57 percent from a year earlier, compared with 93 percent in March, while exports to Chinese bonded areas increased 249 percent year-on-year after rising 343 percent year-on-year in March.
Lian Ping, chief economist at Bank of Communications, said that the real trade surplus in the first four months was surely not as high as indicated by the official figures as the alleged fast export growth was not matched by other economic indicators, including power output, power consumption, factory production and employment levels in the manufacturing sector.
"Arbitraging exchange rate differentials is not the most important way for speculative investors to chase returns. Instead, it's the investments into China's real estate sector and financing platforms, which demand a huge amount of capital, but are controlled by the government," Lian said.
The State Administration of Foreign Exchange said on May 5 that it will boost its scrutiny of export invoices, and impose tougher penalties on companies that provide fake data to crack down on hot money inflows.